Architecture Overview¶
Overall Archtecture Diagram¶
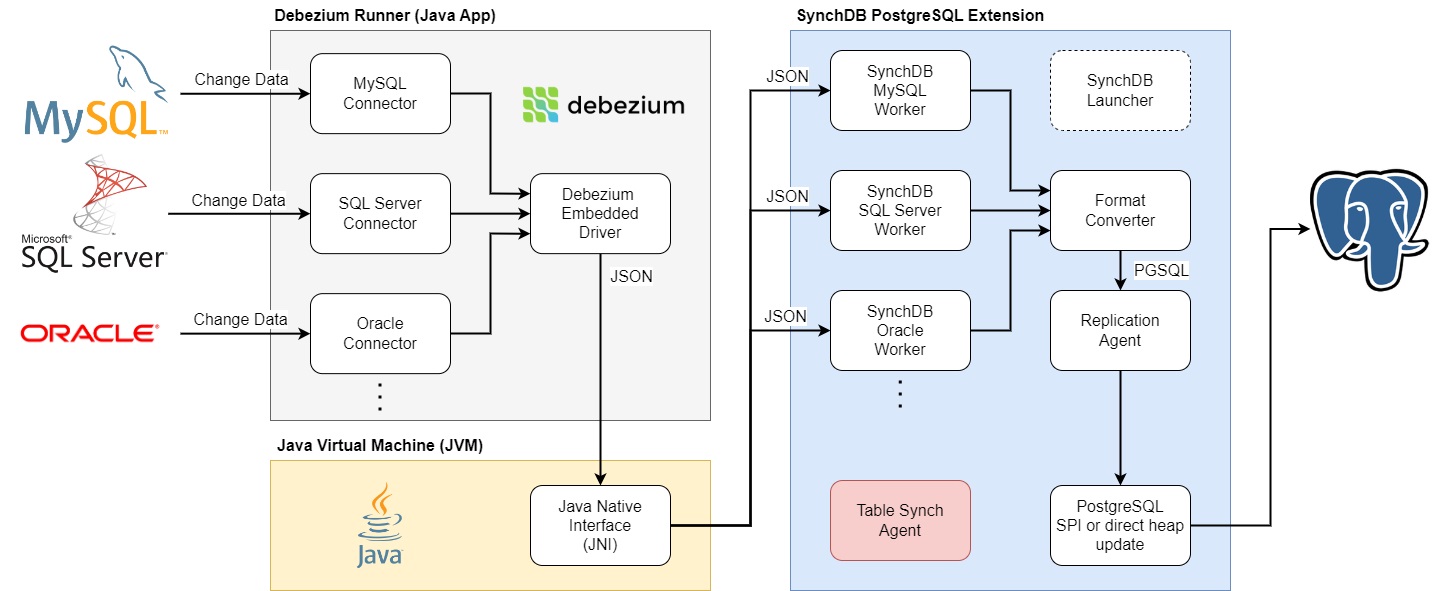
SynchDB extension consists of 2 code spaces (Java and C) with JNI sitting in between them as facilitator.
Debezium Runner - Java
- Debezium Runner Driver
- Embedded Debezium Engine
SynchDB Extension - C
- SynchDB Launcher
- SynchDB Worker
- Format Converter
- Replication Agent
The 2 code spaces are interconnected via Java Native Interface (JNI), which is a framework that allows Java applications to interact with native code written in languages like C or C++ and vice versa. It enables Java programs to call and be called by native applications and libraries, providing a bridge between Java’s platform independence and the performance advantages of native code. JNI is commonly used to integrate platform-specific features, optimize performance-critical sections of an application, or access legacy libraries that are not available in Java. It requires careful management of resources, as it involves switching between the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and native environments, which can introduce complexity.
For this reason, SynchDB requires JNI to exchange resources between Debezium runner engine and SynchDB PostgreSQL extension. JNI is available with Java Installation (ex. openjdk).
Debezium Runner - Java¶
This is the driver program in Java that utilizes the Debezium Embedded Engine with various connectors to different database sources. This is the key underlying components that make logical replication from multiple database vendors possible. Its main responsibility is to connect to the specified remote database and periodically fetch its changes and convert them to a common JSON structure. This JSON structure is then passed down to SynchDB Extension in C to process and eventually apply the changes to PostgreSQL.
Debezium Runner Component Architecture
SynchDB Extension - C¶
This is the main entrypoint that initializes a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and run Debezium Runner on it. It periodically fetches a batch of JSON change events from Debezium Runner, process the data and apply them to PostgreSQL. It is also responsible for notifying Debezium that it has successfully completed a batch of JSON change events so that both components are synchronized in terms of replication progress.