快速入门指南¶
尝试 SynchDB 的最快方法是使用 SynchDB 及其配套源(MySQL、SQL Server、Oracle 等)的预构建 Docker 镜像。使用仓库的 ezdeploy.sh(仅限 Linux)命令,它会通过简单的交互式提示引导您启动所选源以及可选的 Prometheus/Grafana,以便您在几分钟内验证捕获和复制操作。
ezdeploy.sh¶
此工具可从 SynchDB 源码仓库 此处 下载。它需要 docker 和 docker-compose(或 docker compose),并且必须在 Linux 上运行。运行时会打印部署选项列表:
./ezdeploy.sh
----------------------------------
-----> Welcome to ezdeploy! <-----
----------------------------------
please select a quick deploy option:
1) synchdb only
2) synchdb + mysql
3) synchdb + sqlserver
4) synchdb + oracle23ai
5) synchdb + oracle19c
6) synchdb + olr(oracle19c)
7) synchdb + all source databases
8) custom deployment
9) deploy monitoring
10) teardown deployment
enter your selection:
- 仅对于 synchdb 部署,请使用选项
1)。 - 对于 synchdb + 1 个源数据库,请使用选项
2)至6)。 - 对于 synchdb + 所有源数据库,请使用选项
7)。 - 对于 synchdb + 自定义源数据库,请使用选项
8)。 - 对于 prometheus 和 grafana 监控部署,请使用选项
9)。 - 要拆除所有部署,请使用选项
10)。
测试源数据库访问详情¶
MySQL:
- 数据库:inventory
- 模式:N/A
- 用户:mysqluser
- 密码:mysqlpwd
Sqlserver:
- 数据库:testDB
- 模式:dbo
- 用户:sa
- 密码:Password!
Oracle23ai:
- 数据库:FREE
- 模式:c##dbzuser
- 用户:c##dbzuser
- 密码:dbz
Oracle19c:
- 数据库:FREE
- 模式:DBZUSER
- 用户:DBZUSER
- 密码:dbz
Openlog Replicator (OLR):
- 服务名称:ORACLE
使用 psql 访问 Synchdb¶
部署完成后,可以通过以下方式访问 synchdb:
docker exec -it synchdb bash -c "psql -d postgres"
连接后,创建 synchdb 扩展:
CREATE EXTENSION synchdb CASCADE;
创建连接器¶
以下是为每种受支持的源数据库类型创建基本连接器的一些示例。
MySQL:
SELECT synchdb_add_conninfo('mysqlconn',
'mysql',
3306,
'mysqluser',
'mysqlpwd',
'inventory',
'postgres',
'null',
'null',
'mysql');
Sqlserver:
SELECT synchdb_add_conninfo('sqlserverconn',
'sqlserver',
1433,
'sa',
'Password!',
'testDB',
'postgres',
'null',
'null',
'sqlserver');
Oracle23ai:
SELECT synchdb_add_conninfo('oracleconn',
'oracle',
1521,
'c##dbzuser',
'dbz',
'FREE',
'postgres',
'null',
'null',
'oracle');
Oracle19c:
SELECT synchdb_add_conninfo('ora19cconn',
'ora19c',
1521,
'DBZUSER',
'dbz',
'FREE',
'postgres',
'null',
'null',
'oracle');
OLR(Oracle19c):
SELECT synchdb_add_conninfo('olrconn',
'ora19c',
1521,
'DBZUSER',
'dbz',
'FREE',
'postgres',
'null',
'null',
'olr');
SELECT synchdb_add_olr_conninfo('olrconn',
'OpenLogReplicator',
7070,
'ORACLE');
查看已创建的连接器:
SELECT * FROM synchdb_conninfo;
有关创建连接器的更多详细信息,请参阅此处
创建对象映射¶
默认情况下,源数据库名称将映射到目标数据库中的架构名称。可以使用对象映射来更改此架构名称。让我们从基于 Oracle 的连接器中更改“orders”表的目标架构,其余部分保留默认值。
SELECT synchdb_add_objmap('oracleconn','table','free.c##dbzuser.orders','oracle23ai.orders');
SELECT synchdb_add_objmap('ora19cconn','table','free.dbzuser.orders','oracle19c.orders');
SELECT synchdb_add_objmap('olrconn','table','free.dbzuser.orders','olr.orders');
有关创建对象映射的更多详细信息,请参见[此处](https://docs.synchdb.com/zh/user-guide/object_mapping_rules/)
创建 JMX 导出器 - 可选¶
以下是一些启用 JMX 导出器进行监控的示例(如果已通过 ezdeploy.sh 预先部署了 Prometheus + Grafana):
MySQL:
SELECT synchdb_add_jmx_exporter_conninfo(
'mysqlconn',
'/home/ubuntu/jmx_prometheus_javaagent-1.3.0.jar',
9404,
'/home/ubuntu/jmxexport.conf');
Sqlserver:
SELECT synchdb_add_jmx_exporter_conninfo(
'sqlserverconn',
'/home/ubuntu/jmx_prometheus_javaagent-1.3.0.jar',
9405,
'/home/ubuntu/jmxexport.conf');
Oracle23ai:
SELECT synchdb_add_jmx_exporter_conninfo(
'oracleconn',
'/home/ubuntu/jmx_prometheus_javaagent-1.3.0.jar',
9406,
'/home/ubuntu/jmxexport.conf');
Oracle19c:
SELECT synchdb_add_jmx_exporter_conninfo(
'ora19cconn',
'/home/ubuntu/jmx_prometheus_javaagent-1.3.0.jar',
9407,
'/home/ubuntu/jmxexport.conf');
关于创建 JMX Exporter 的更多详细信息,请参见此处
启动连接器¶
MySQL:
SELECT synchdb_start_engine_bgw('mysqlconn');
Sqlserver:
SELECT synchdb_start_engine_bgw('sqlserverconn');
Oracle23ai:
SELECT synchdb_start_engine_bgw('oracleconn');
Oracle19c:
SELECT synchdb_start_engine_bgw('ora19cconn');
OLR(Oracle19c):
SELECT synchdb_start_engine_bgw('olrconn');
有关连接器启动的更多详细信息,请参见[此处](https://docs.synchdb.com/zh/user-guide/start_stop_connector/)
检查连接器运行状态¶
使用“synchdb_state_view()”检查所有连接器的运行状态。
SELECT * FROM synchdb_state_view;
以下是输出示例:
postgres=# SELECT * FROM synchdb_state_view;
name | connector_type | pid | stage | state | err | last_dbz_offset
---------------+----------------+--------+------------------+---------+----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sqlserverconn | sqlserver | 579820 | initial snapshot | polling | no error | {"commit_lsn":"0000006a:00006608:0003","snapshot":true,"snapshot_completed":false}
mysqlconn | mysql | 579845 | initial snapshot | polling | no error | {"ts_sec":1741301103,"file":"mysql-bin.000009","pos":574318212,"row":1,"server_id":223344,"event":2}
oracleconn | oracle | 580053 | initial snapshot | polling | no error | offset file not flushed yet
ora19cconn | oracle | 593421 | initial snapshot | polling | no error | offset file not flushed yet
olrconn | oracle | 601235 | initial snapshot | polling | no error | offset file not flushed yet
(5 rows)
有关运行状态的更多信息,请参见此处,以及运行统计信息,请参见此处。
检查初始快照中的表和数据¶
默认情况下,连接器将执行“初始”快照,以捕获表模式和初始数据,然后转换并将它们应用到不同“模式”下的 PostgreSQL。您应该看到类似以下内容:
MySQL:
\dt inventory.*
\dt inventory.*
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
-----------+------------------+-------+--------
inventory | addresses | table | ubuntu
inventory | customers | table | ubuntu
inventory | geom | table | ubuntu
inventory | orders | table | ubuntu
inventory | products | table | ubuntu
inventory | products_on_hand | table | ubuntu
(6 rows)
Sqlserver:
\dt testdb.*
\dt testdb.*
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------------------+-------+--------
testdb | customers | table | ubuntu
testdb | orders | table | ubuntu
testdb | products | table | ubuntu
testdb | products_on_hand | table | ubuntu
(4 rows)
Oracle23ai
\dt oracle23ai.*
\dt oracle23ai.*
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
------------+--------+-------+--------
oracle23ai | orders | table | ubuntu
(1 row)
Oracle19c
\dt oracle19c.*
\dt oracle19c.*
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
-----------+--------+-------+--------
oracle19c | orders | table | ubuntu
(1 row)
OLR
\dt olr.*
\dt olr.*
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+--------+-------+--------
olr | orders | table | ubuntu
(1 row)
模拟 INSERT 事件并观察变更数据捕获 (CDC)¶
我们可以使用 docker exec 为每种连接器类型模拟一次 INSERT 操作,并观察变更数据捕获 (CDC)。
MySQL:
docker exec -i mysql mysql -D inventory -umysqluser -pmysqlpwd -e "INSERT INTO orders(order_date, purchaser, quantity, product_id) VALUES ('2025-12-12', 1002, 10000, 102)"
postgres=# SELECT * from inventory.orders;
order_number | order_date | purchaser | quantity | product_id
--------------+------------+-----------+----------+------------
10001 | 2016-01-16 | 1001 | 1 | 102
10002 | 2016-01-17 | 1002 | 2 | 105
10003 | 2016-02-19 | 1002 | 2 | 106
10004 | 2016-02-21 | 1003 | 1 | 107
10005 | 2025-12-12 | 1002 | 10000 | 102
(5 rows)
Sqlserver:
docker exec -i sqlserver /opt/mssql-tools18/bin/sqlcmd -U sa -P 'Password!' -d testDB -C -Q "INSERT INTO orders(order_date, purchaser, quantity, product_id) VALUES ('2025-12-12', 1002, 10000, 102)"
postgres=# SELECT * from testdb.orders;
order_number | order_date | purchaser | quantity | product_id
--------------+------------+-----------+----------+------------
10001 | 2016-01-16 | 1001 | 1 | 102
10002 | 2016-01-17 | 1002 | 2 | 105
10003 | 2016-02-19 | 1002 | 2 | 106
10004 | 2016-02-21 | 1003 | 1 | 107
10005 | 2025-12-12 | 1002 | 10000 | 102
(5 rows)
Oracle23ai:
echo -ne "INSERT INTO orders(order_number, order_date, purchaser, quantity, product_id) VALUES (10005, TO_DATE('2025-12-12', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 1002, 10000, 102);\n" | docker exec -i oracle sqlplus c##dbzuser/dbz@//localhost:1521/FREE
postgres=# SELECT * FROM oracle23ai.orders;
order_number | order_date | purchaser | quantity | product_id
--------------+---------------------+-----------+----------+------------
10001 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10002 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10003 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10004 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10005 | 2025-12-12 00:00:00 | 1002 | 10000 | 102
(5 rows)
Oracle19c:
echo -ne "INSERT INTO orders(order_number, order_date, purchaser, quantity, product_id) VALUES (10005, TO_DATE('2025-12-12', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 1002, 10000, 102);\n" | docker exec -i ora19c sqlplus DBZUSER/dbz@//localhost:1521/FREE
postgres=# SELECT * FROM oracle19c.orders;
order_number | order_date | purchaser | quantity | product_id
--------------+---------------------+-----------+----------+------------
10001 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10002 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10003 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10004 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10005 | 2025-12-12 00:00:00 | 1002 | 10000 | 102
(5 rows)
OLR:
echo -ne "INSERT INTO orders(order_number, order_date, purchaser, quantity, product_id) VALUES (10005, TO_DATE('2025-12-12', 'YYYY-MM-DD'), 1002, 10000, 102);\n" | docker exec -i ora19c sqlplus DBZUSER/dbz@//localhost:1521/FREE
postgres=# SELECT * FROM olr.orders;
order_number | order_date | purchaser | quantity | product_id
--------------+---------------------+-----------+----------+------------
10001 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10002 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10003 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10004 | 2024-01-01 00:00:00 | 1003 | 2 | 107
10005 | 2025-12-12 00:00:00 | 1002 | 10000 | 102
(5 rows)
Grafana 上的连接器指标 - 可选¶
如果您选择使用 ezdeploy.sh 部署监控,并在启动连接器之前调用了可选的 synchdb_add_jmx_exporter_conninfo(),则连接器指标将在 Grafana 上可用。
- 访问 Grafana: http://localhost:3000/
- 默认登录名: admin/admin (首次登录时需要更改密码)
导航到仪表板菜单:
选择所需模板:
- Java 虚拟机 - JVM 资源信息
- SynchDB MySQL 仪表板 - MySQL 连接器信息
- SynchDB SQLServer 仪表板 - SQLServer 连接器信息
- SynchDB Oracle 仪表板 - Oracle 连接器信息
选择所需实例: 每个启用 JMX 导出器的连接器都绑定到一个专用端口号,以便 Prometheus 可以从中获取数据。使用实例下拉菜单按端口号选择连接器。
Java 虚拟机仪表板:
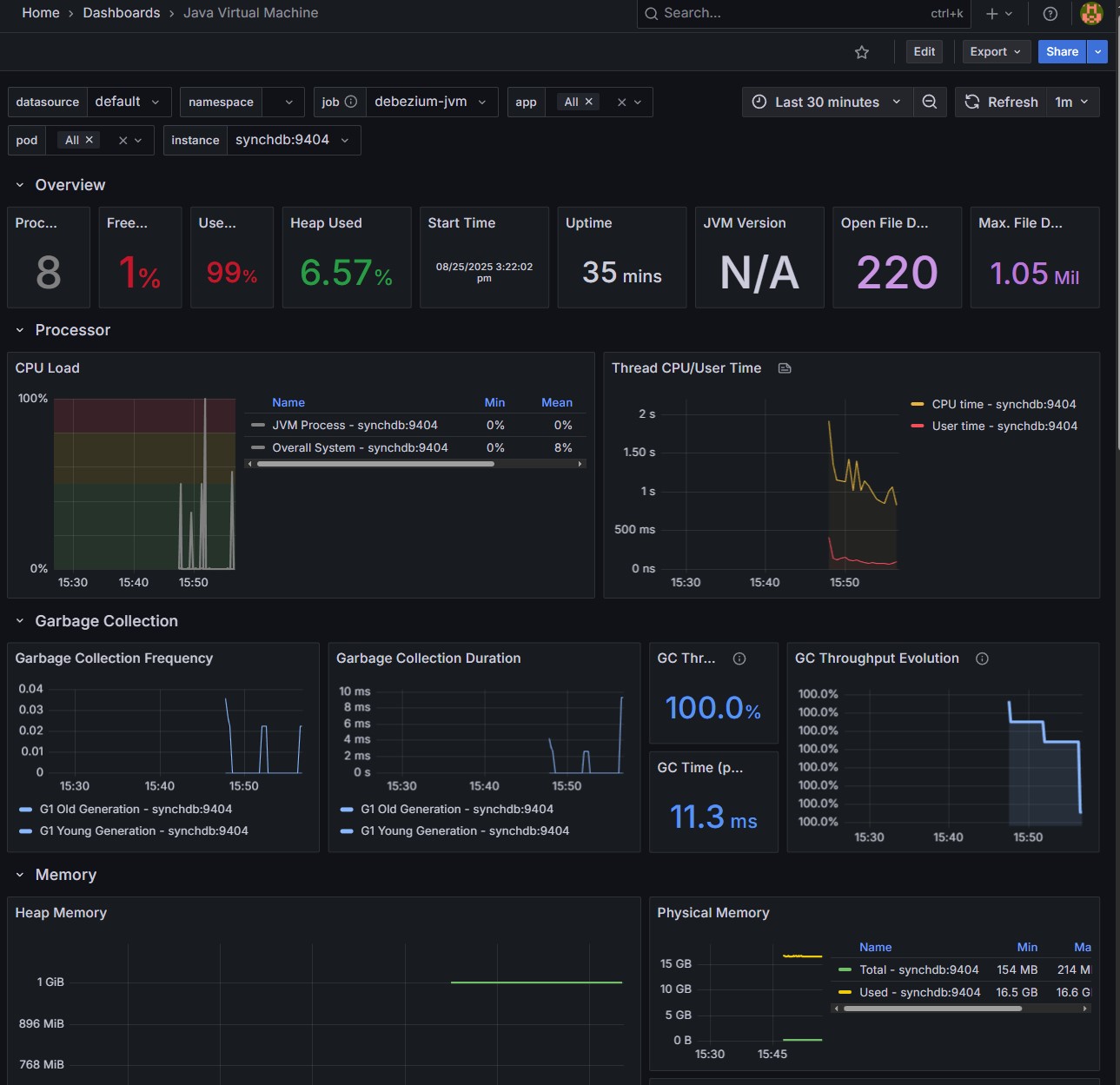
MySQL 仪表板:
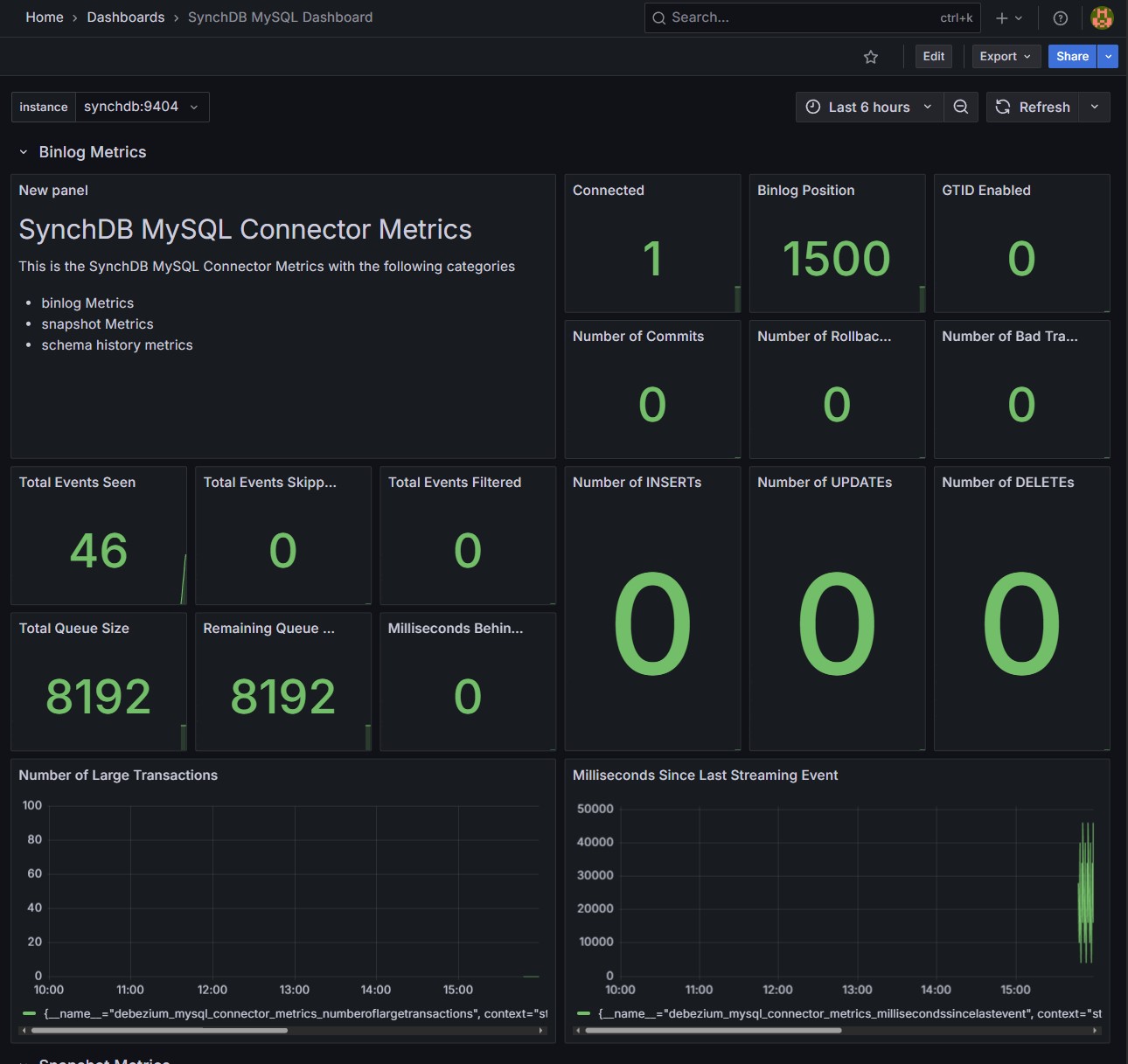
SQLServer 仪表板:
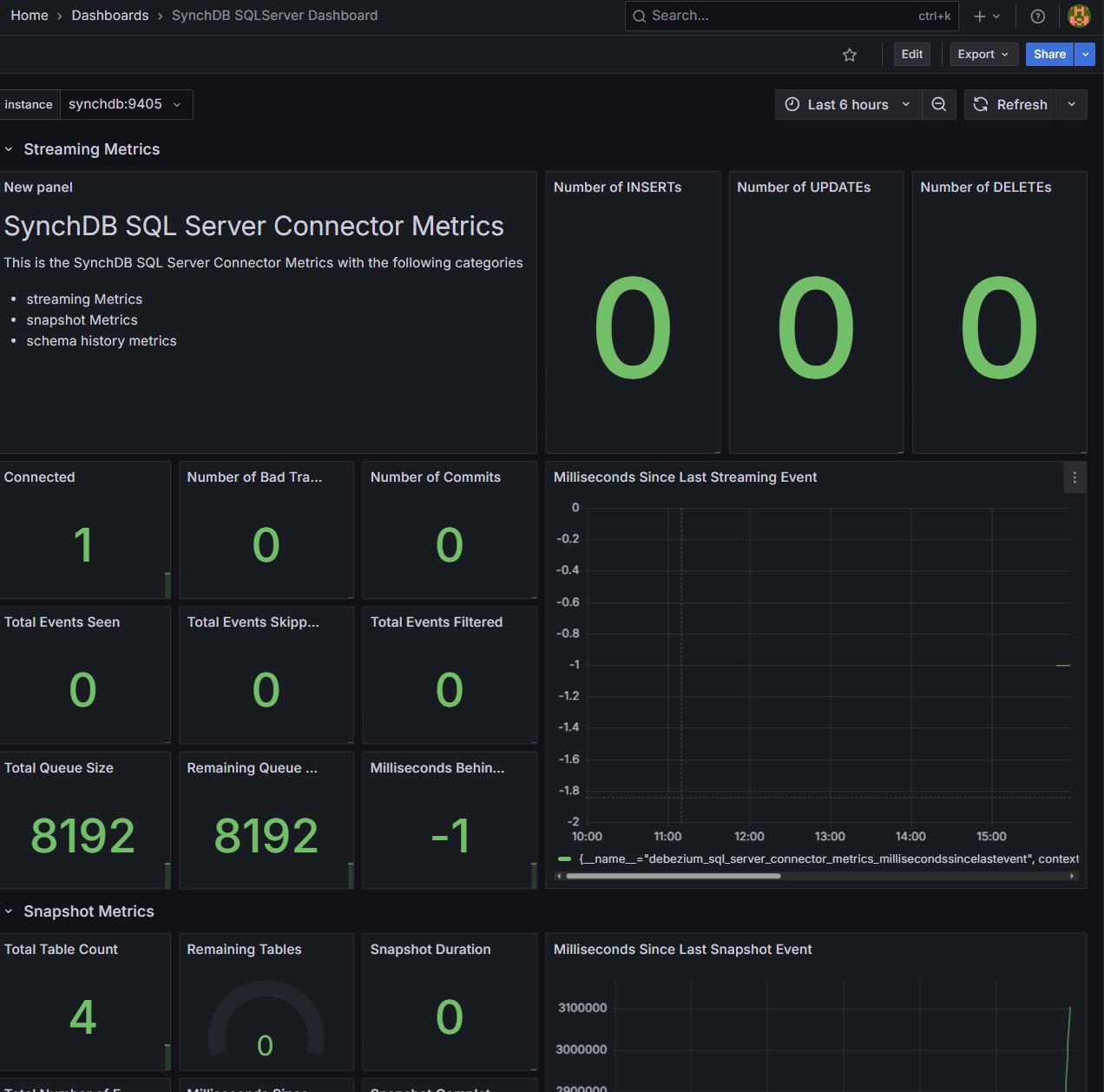
Oracle 仪表板:
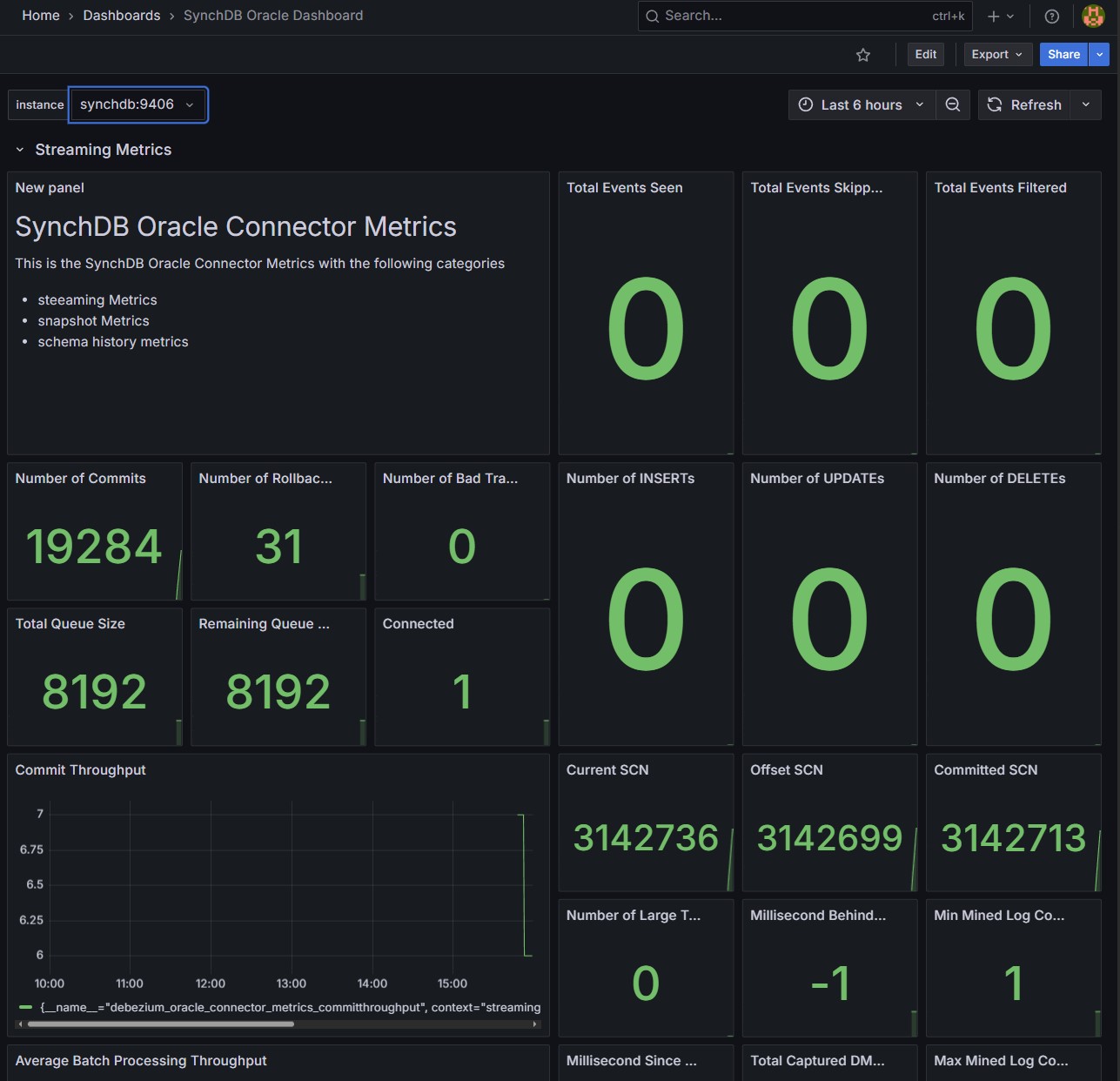
停止并移除连接器¶
MySQL:
SELECT synchdb_stop_engine_bgw('mysqlconn');
SELECT synchdb_del_conninfo('mysqlconn');
Sqlserver:
SELECT synchdb_stop_engine_bgw('sqlserverconn');
SELECT synchdb_del_conninfo('sqlserverconn');
Oracle23ai:
SELECT synchdb_stop_engine_bgw('oracleconn');
SELECT synchdb_del_conninfo('oracleconn');
Oracle19c:
SELECT synchdb_stop_engine_bgw('ora19cconn');
SELECT synchdb_del_conninfo('ora19cconn');
OLR(Oracle19c):
SELECT synchdb_stop_engine_bgw('olrconn');
SELECT synchdb_del_conninfo('olrconn');