JMX MBEAN Monitoring¶
JMX (Java Management Extensions)¶
JMX, or Java Management Extensions, is a Java technology that provides tools for managing and monitoring applications, system objects, devices, and service-oriented networks. It allows developers to expose application information and enables external tools to access and interact with this information for monitoring and management purposes.
JMX MBean for Debezium¶
Debezium connectors expose metrics via the MBean name for the connector with MBean tag equals to the connector name. These metrics, which are specific to each connector instance, provide data about the behavior of the connector’s snapshot, streaming, and schema history processes.
Enable JMX on a Connector with synchdb_add_jmx_conninfo() or disable with synchdb_del_jmx_conninfo()¶
The synchdb_add_jmx_conninfo() and synchdb_del_jmx_conninfo() functions adds or deletes JMX monitoring configuration to or from an existing connector. This enables runtime monitoring and diagnostics via tools like JConsole.
Function Signature
synchdb_add_jmx_conninfo(
name text,
jmx_listenaddr text,
jmx_port integer,
jmx_rmiserveraddr text,
jmx_rmiport integer,
jmx_auth boolean,
jmx_auth_passwdfile text,
jmx_auth_accessfile text,
jmx_ssl boolean,
jmx_ssl_keystore text,
jmx_ssl_keystore_pass text,
jmx_ssl_truststore text,
jmx_ssl_truststore_pass text
)
synchdb_del_jmx_conninfo(
name text
)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
(text) The name of the existing connector to which JMX configuration should be added. Must already exist in synchdb_conninfo. |
jmx_listenaddr |
(text) The IP address on which the JVM will listen for JMX connections. Use '0.0.0.0' to listen on all network interfaces, or specify a specific IP. |
jmx_port |
(integer) The local port for JMX communication (used for client discovery). Must be open and not in use. |
jmx_rmiserveraddr |
(text) The public/external IP address used by remote JMX clients (e.g., JConsole) to connect to the JVM. Usually set to the host machine’s external IP. |
jmx_rmiport |
(integer) The RMI server port used for actual JMX object communication. This must also be open in firewall and network settings. Usually the same as jmx_port. |
jmx_auth |
(boolean) Enable authentication for JMX? If true, clients must provide a username/password stored in the files below. |
jmx_auth_passwdfile |
(text) Path to the password file used for JMX authentication. If not using authentication, pass 'null'. |
jmx_auth_accessfile |
(text) Path to the access control file defining roles (e.g., monitor, control). Required only if authentication is enabled. If not using authentication, pass 'null' |
jmx_ssl |
(boolean) Enable SSL encryption for JMX connections? Set to true to secure communication. |
jmx_ssl_keystore |
(text) Path to the keystore file (in JKS format) containing the server’s private key and certificate. Required if jmx_ssl = true. |
jmx_ssl_keystore_pass |
(text) Password for the keystore file. |
jmx_ssl_truststore |
(text) Path to the truststore (JKS) that holds trusted CA certificates. Used to verify client identities if mutual TLS is configured. |
jmx_ssl_truststore_pass |
(text) Password for the truststore file. |
Password and Access Files for JMX Authentication¶
When enabling JMX authentication in your JVM configuration (i.e., setting jmx_auth = true), you must provide two files:
Password File:¶
This file stores valid JMX usernames and their corresponding passwords.
Format:
# Format: username password
<username> <password>
Example:
monitorRole mySecretPassword
controlRole anotherSecretPassword
monitorRole and controlRole are example usernames. Replace mySecretPassword and anotherSecretPassword with strong passwords of your choice. You can define multiple users.
Access File:¶
This file defines what each user is allowed to do via JMX. Possible access levels:
- readonly – can view MBeans but not modify them.
- readwrite – can both view and modify MBeans.
Format:
# Format: username access_level
<username> <access>
Example:
monitorRole readonly
controlRole readwrite
File Permissions:¶
Make sure both files are owned by the user running the JVM, and have restricted permissions:
chmod 600 jmxpwd.file jmxacc.file
chown youruser:youruser jmxpwd.file jmxacc.file
synchdb_add_jmx_conninfo Examples¶
Enable JMX MBean with no authentication and no SSL:
SELECT synchdb_add_jmx_conninfo(
'mysqlconn', -- existing connector name
'0.0.0.0', -- JMX listen address
9010, -- JMX listen port
'10.55.13.17', -- JMX RMI server address - for remote client connect
9010, -- JMX RMI server port - for remoet client connect
false, -- use authentication?
'null', -- password file for authentication
'null', -- access file for authentication
false, -- use SSL?
'null', -- SSL keystore path
'null', -- SSL keystore password
'null', -- SSL trust store
'null'); -- SSL trust store password
Enable JMX MBean with authentication
SELECT synchdb_add_jmx_conninfo(
'mysqlconn', -- existing connector name
'0.0.0.0', -- JMX listen address
9010, -- JMX listen port
'10.55.13.17', -- JMX RMI server address - for remote client connect
9010, -- JMX RMI server port - for remoet client connect
true, -- use authentication?
'/path/to/passwd.file', -- password file for authentication
'/path/to/access.file', -- access file for authentication
false, -- use SSL?
'null', -- SSL keystore path
'null', -- SSL keystore password
'null', -- SSL trust store
'null'); -- SSL trust store password
Enable JMX MBean with authentication and SSL without SSL client verify
SELECT synchdb_add_jmx_conninfo(
'mysqlconn', -- existing connector name
'0.0.0.0', -- JMX listen address
9010, -- JMX listen port
'10.55.13.17', -- JMX RMI server address - for remote client connect
9010, -- JMX RMI server port - for remoet client connect
true, -- use authentication?
'/path/to/passwd.file', -- password file for authentication
'/path/to/access.file', -- access file for authentication
true, -- use SSL?
'/path/to/keystore', -- SSL keystore path
'keystorepass', -- SSL keystore password
'null', -- SSL trust store
'null'); -- SSL trust store password
Enable JMX MBean with authentication and SSL + SSL client verify
SELECT synchdb_add_jmx_conninfo(
'mysqlconn', -- existing connector name
'0.0.0.0', -- JMX listen address
9010, -- JMX listen port
'10.55.13.17', -- JMX RMI server address - for remote client connect
9010, -- JMX RMI server port - for remoet client connect
true, -- use authentication?
'/path/to/passwd.file', -- password file for authentication
'/path/to/access.file', -- access file for authentication
true, -- use SSL?
'/path/to/keystore', -- SSL keystore path
'keystorepass', -- SSL keystore password
'/path/to/truststore', -- SSL trust store
'truststorepass'); -- SSL trust store password
Visualize JMX metrics with jconsole¶
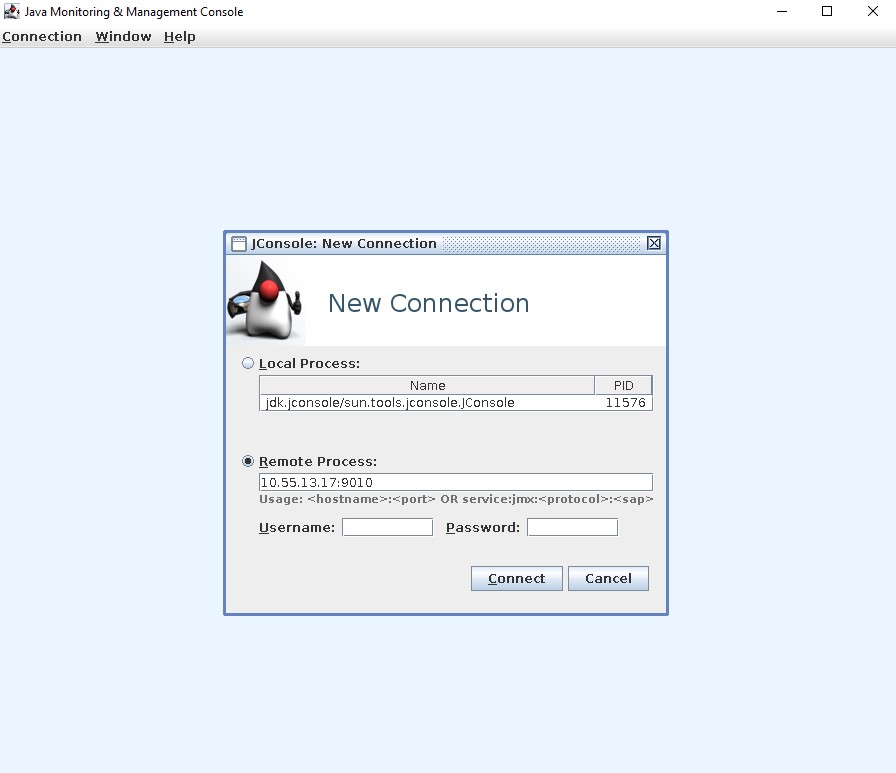
When a connector with JMX configuration is started, the JMX service will be running on the designated port number. We can use jconsole that comes with Java distribution to connect to JMX server. It is possible to connect locally via the JVM (connector worker) PID or via IP address and port number. If authentication is enabled, username and password are required as well. If no authentication is used, these can be left empty.
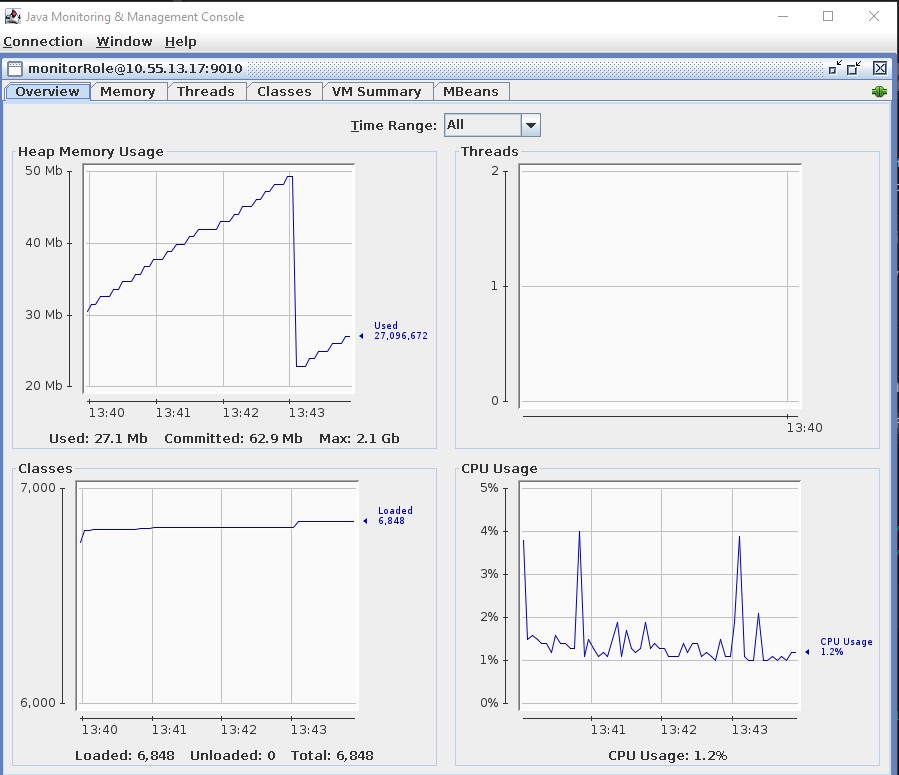
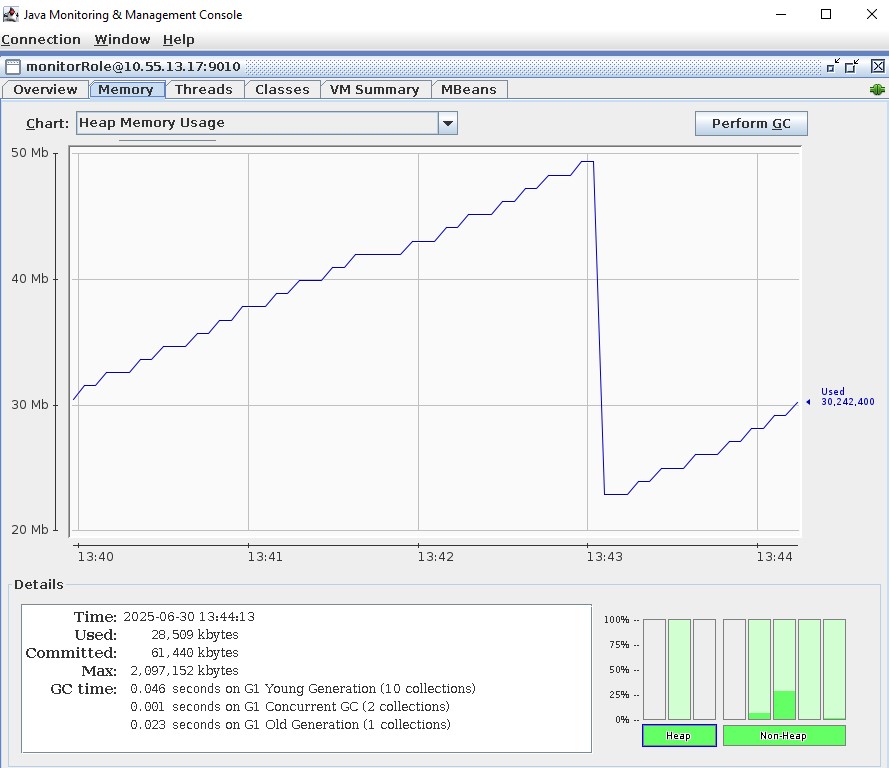
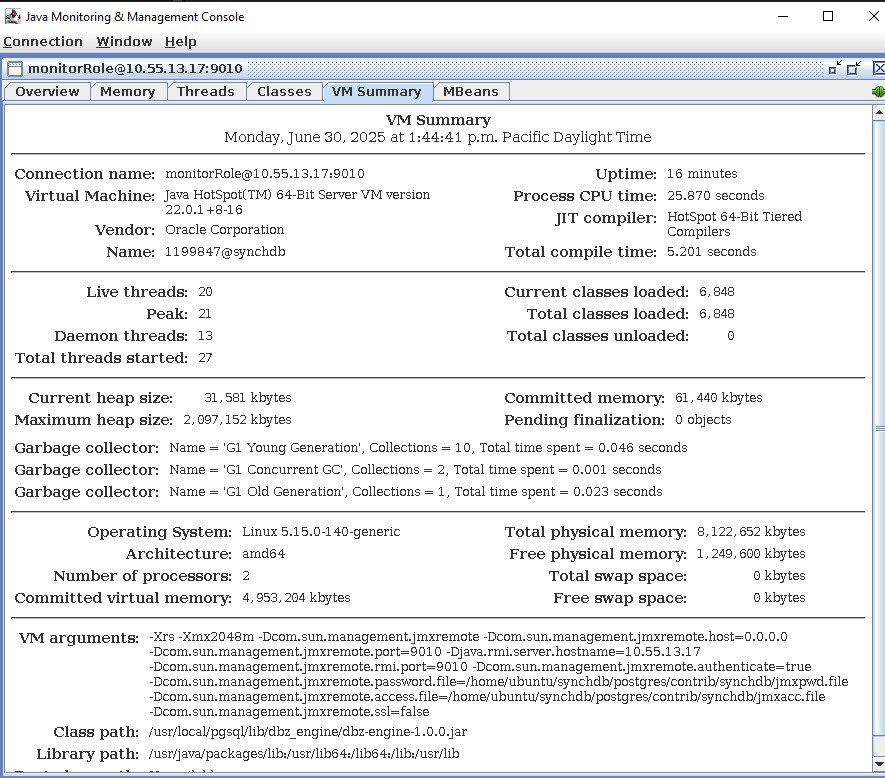
Once connected, we can view all the details about JVM's operating metrics such as CPU, memory, class utilization, threads...etc.
Visualize Debezium JMX MBeans¶
The last tab is MBeans, which contains the Debezium specific metrics for schema history, snapshot and streaming stages.
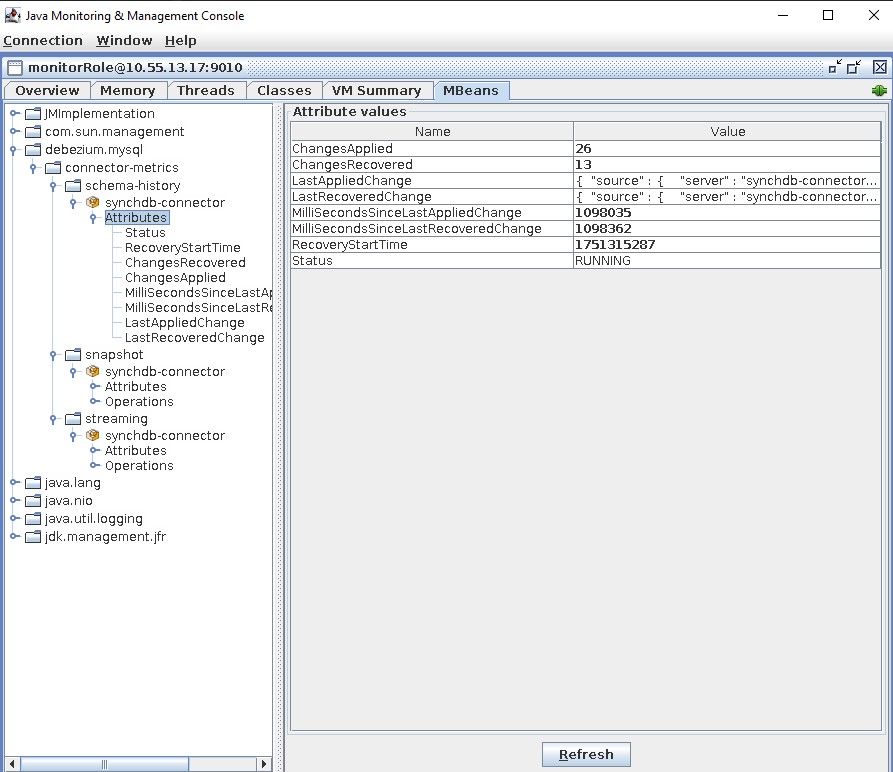
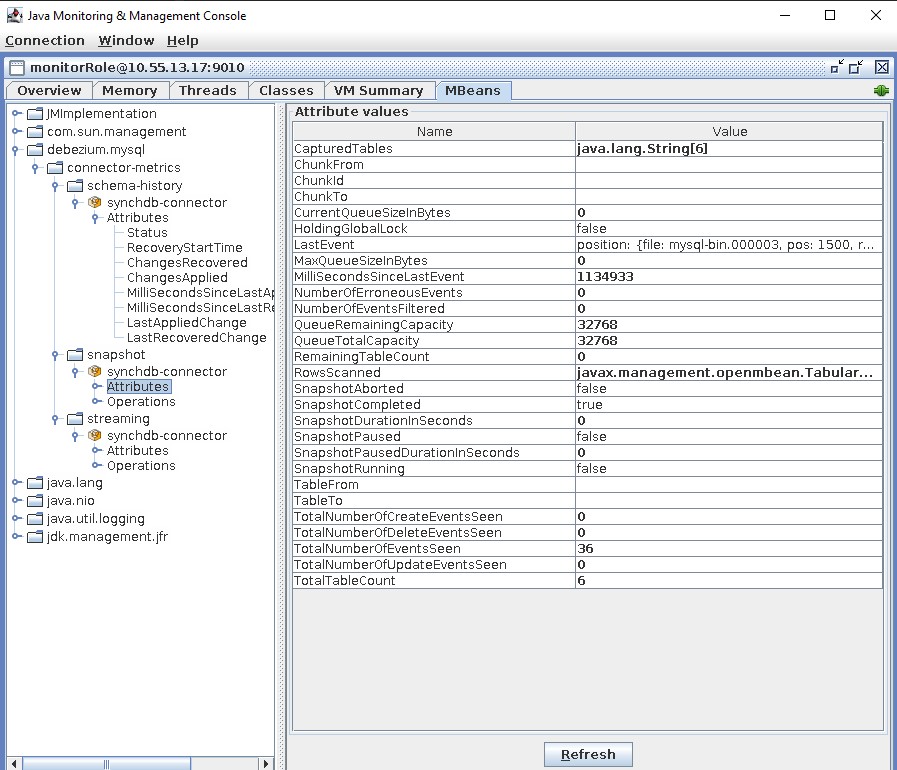
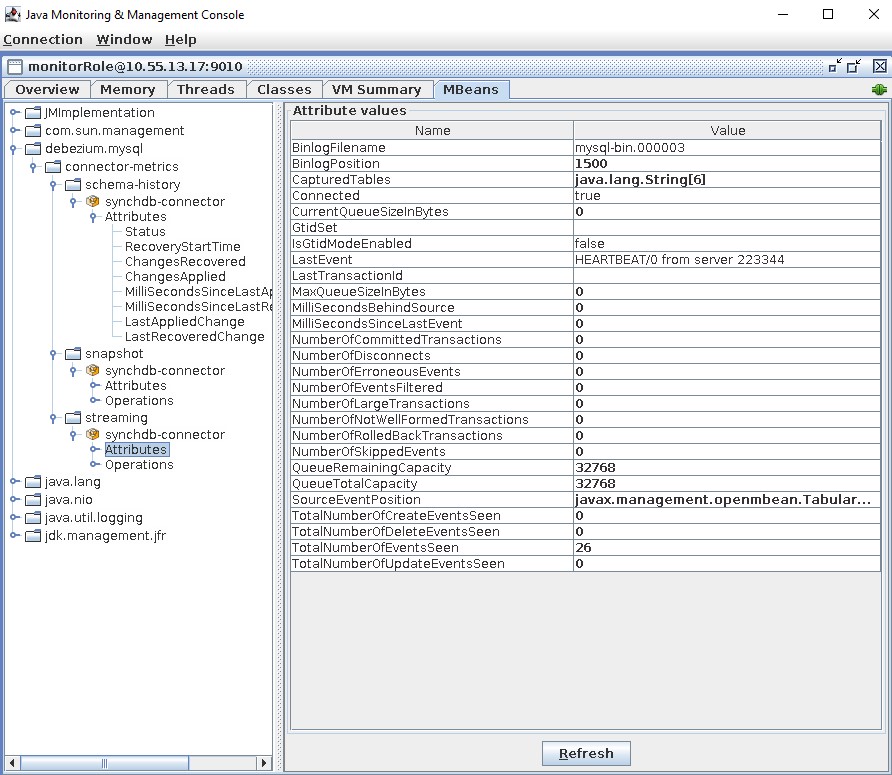
Based on the connector type, the MBean metrics may be different. Refer to Debezium connector documentation on the list of metrics captured: